6.2.5.4 Frequency spectrum UMTS/IMT-2000
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) is the European contribution to IMT-2000, the worldwide mobile communications system of the third generation. Mobile radio communications systems of the first generation are analogue systems, such as the D network in Austria. GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is the most successful representative of mobile communications systems of the second generation. With more than 640 million subscribers (source: GSM Association, December 2001), GSM, which is standardised in Europe, has spread far beyond Europe.
UMTS/IMT-2000 is to be implemented as of the end of 2002. It shall offer data rates that go far beyond those of current mobile systems. As a result, mobile multimedia applications (integration of voice, image and data communications) will be implemented.
IMT-2000 consists of a terrestrial system and a satellite system. The satellite system will facilitate mobile communications especially in those places where a terrestrial coverage is not available. The activities on the European and national levels currently focus mainly on the terrestrial component. Moreover, the terrestrial component of UMTS is being discussed.
For Europe the frequency bands for UMTS/IMT-2000 are defined in the decisions
ERC/DEC/(97)07 and ERC/DEC(99)25.
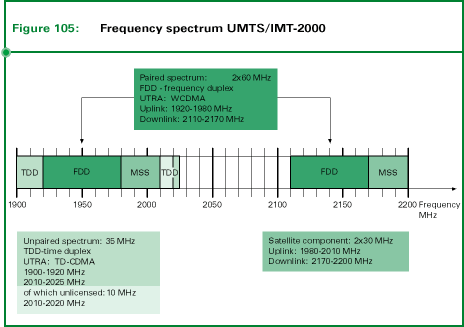
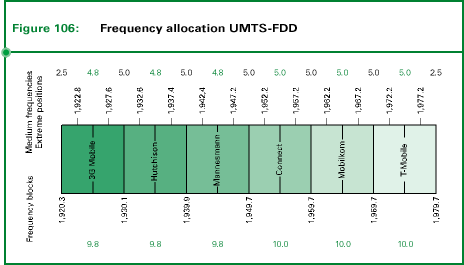
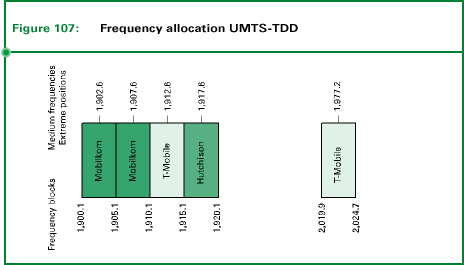
For the terrestrial part of UMTS/IMT-2000 a total of 155 MHz have been
set aside. Of these, the ranges 1920 to 1980 MHz as well as 2210 to 2170 MHz,
i.e. 2 x 60 MHz, can be used as paired frequency bands, and the ranges
1900 to 1920 MHz as well as 2010 to 2020 MHz are reserved for "non-licensed"
applications. The range 2010 to 2020 MHz is therefore not available for
assignment to operators in states that are transposing the relevant ERC
decision. This means that 145 MHz (2 x 60 MHz + 25 MHz) can be assigned
to operators.
Probably, as from 2008, additional frequencies (UMTS extension bands)
will be available in the 2.5 to 2.69 GHz range.
UMTS, like GSM, will offer speech and data services. However, UMTS allows for higher data rates and shorter delays due to the more advanced radio interface. WAP and i-mode are protocols which use the GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) data service. Messaging services like MMS (Multimedia Messaging Services) can be transmitted by means of such applications. As a further expansion of SMS (Short Message Service), which is intensively used today, MMS allows to send and receive sounds and images in "multimedia" e-mails.
IMT-2000 (International Mobile Telecommunications) is the worldwide mobile communications system of the third generation. The ITU is responsible for standardising IMT-2000. IMT-2000 will combine different mobile communications systems of the third generation in the framework of a family design. "Roaming" will, however, be possible between the different systems.
UMTS, the European contribution to IMT-2000, was standardised by ETSI, together with other standardising institutes in the framework of 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project). In January 1998, ETSI took a decision regarding the radio interfaces for UMTS. The radio interface UTRA (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access) comprises W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) for operation in the FDD mode (Frequency Division Duplex) and TD-CDMA (Time Division Code Division Multiple Access) for operation in the TDD mode (Time Division Duplex). The data rates of UMTS are said to be 144 kbit/s, as a minimum, in rural areas, and 384 kbit/s in urban areas. The frequently mentioned data rate of 2 Mbit/s is a theoretical maximum value which will not be relevant in practice.
For both access methods (W-CDMA and TD-CDMA) the bandwidth taken up by a channel is approx. 5 MHz.